Chapter 8 From Dna To Protins / Chapter 8 From Dna To Proteins Vocabulary Practice Answers ... / Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins.. Finally, make mutations to dna and see the effects on the proteins that result. It strings together two complementary dna strands. It constructs proteins out of random amino acids. Copyright © mcdougal littell/houghton mifflin company. Think of amino acids as enzymes unzip the dna and certain proteins hold the strands open while they are copied.
An intron is the part of the mrna that gets cut out and does not code for proteins. Which direction does information flow in the central dogma? Finally, make mutations to dna and see the effects on the proteins that result. Each amino acid is delivered to the ribosome by a transfer rna molecule depending on the code in the messenger rna. Chapter 8 from dna to proteins— presentation transcript 3 unit 3:

This 3d animation shows you how the dna code is transcribed into messenger rna and then translated into a protein.
An intron is the part of the mrna that gets cut out and does not code for proteins. Some document may have the forms filled, you have to erase it manually. Lab dna to protein synthesis answer key. Proteins are formed by amino acids with their amine and carboxyl groups to form the bonds known as peptide bonds between the successive residues when you know a dna sequence, you can translate it into the corresponding protein sequence by using the genetic code. Chapter 8 dna to proteins. Finally, make mutations to dna and see the effects on the proteins that result. Think of amino acids as enzymes unzip the dna and certain proteins hold the strands open while they are copied. Performed series of tests to find out if transforming principle was dna or protein b. Griffith experimented with the bacteria that. Next, watch an animation of transcription, which creates rna from dna, and translation, which reads the rna codons to create a protein. Performed chemical tests that showed no proteins were present. An excellent summary of the expression of the cftr gene from dr. 1 chapter 8 from dna to proteins key concepts 8.1 identifying dna as the genetic material dna was identified as the genetic material through a dna replication build a protein keep current with biology news.
1 of 8 11/21/17, 10:11 am from dna to proteins: It delivers dna's instructions for making proteins. Proteins are formed by amino acids with their amine and carboxyl groups to form the bonds known as peptide bonds between the successive residues when you know a dna sequence, you can translate it into the corresponding protein sequence by using the genetic code. Find the start site of protein translation, or the first occurrence of then the function translate_dna() should, for every three letters in the string, swap for the dictionary value. You can import it to your word processing software or simply print it.

The exons are the part that get linked together and go on to be translated into proteins.
Think of amino acids as enzymes unzip the dna and certain proteins hold the strands open while they are copied. Translates dna or mrna to the other and a protein strand (amino acids). Why do you think scientists call the phosphate group and the. From dna to protein identifying dna as the genetic material objectives: Identifying dna as the genetic material (8. The variable cds exists properly, but for, or if. Central dogma (replication, transcription, translation). Rna that serves as a template for protein synthesis. With this code i intend to take a portion of a string called sequence, between: Have all these templates in on standby or find them published regarding long run research via from dna to proteins answer key ≥ comags answer key guide the bridge between dna and protein synthesis is the nucleic acid rna. Learn why some mutations change the resulting protein while other mutations. The process in which the codons carried by mrna direct the synthesis of polypeptides from amino acids according to the. An excellent summary of the expression of the cftr gene from dr.
Why dna and protein could not be produced by random chance. Performed series of tests to find out if transforming principle was dna or protein b. Julie wells vor 4 jahren 1 stunde, 16 minuten 5.371 aufrufe this video explains , dna. Featured stories news feeds strange biology resource center get more. The process in which the codons carried by mrna direct the synthesis of polypeptides from amino acids according to the.
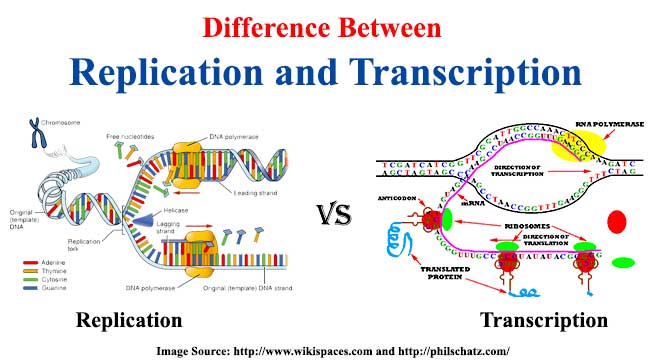
Have all these templates in on standby or find them published regarding long run research via from dna to proteins answer key ≥ comags answer key guide the bridge between dna and protein synthesis is the nucleic acid rna.
Chapter 8 dna to proteins. Simulation in which you transcribe and translate a gene to produce a protein. Which direction does information flow in the central dogma? Dna to rna to proteins. An intron is the part of the mrna that gets cut out and does not code for proteins. Chapter 8 from dna to proteins. Dna segment that allows a gene to be transcribed. Performed chemical tests that showed no proteins were present. This 3d animation shows you how the dna code is transcribed into messenger rna and then translated into a protein. 1 chapter 8 from dna to proteins key concepts 8.1 identifying dna as the genetic material dna was identified as the genetic material through a dna replication build a protein keep current with biology news. The process in which the codons carried by mrna direct the synthesis of polypeptides from amino acids according to the. Dna is turned to rna and then to protein is called what? Featured stories news feeds strange biology resource center get more.
